CLASS OBJECTIVE
Learn the third programming structure named Loop, to create repetitive procedures, using Raptor to create lists of numeric series.
2nd PERIOD NOTEBOOK COVER
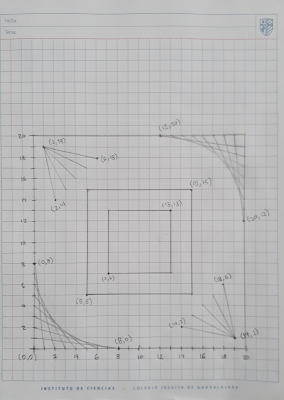
As always, you'll have to create your notebook cover, but this time you're going to use a Cartesian Plane to draw some lines and boxes. This will help you understand our next topic, the Raptor Graphic Window in which we'll use X and Y dimensions (coordinates).
Besides, don't forget to include the next elements. You can use the upper section of your cover.
- Your full name, list number and group
- PERIOD 2, in big size letters
- RAPTOR GRAPHIC WINDOW, also big size letters
- The Cartesian Plane below
Turn the page and, behind the cover, write down the Evaluation Criteria
- Class Activities 45%
- Homeworks 15%
- Attitude 10%
- Summative Evaluation 30%
INTRODUCTION
You've learned that when creating an algorithm, the program can execute all the instructions one by one until the end. We called this sequential coding.
Then, you learned to use decisions to create differents paths of coding, which means that not all the steps of the program will be executed. This decision are represented by the rhombus figure.
In this class, you'll learn to create repetitive procedures, in other words, coding that is executed as many times as needed. This kind of programming is called Loop.
Obviously, in Raptor you can drag the loop symbol from the left panel and place it in the algorithm.
In the example, there's a variable named contador which initially contains the number 1. When the algorithm enters the loop, contador will be shown, then it'll increse by two using an assignment symbol. This means that contador no longer contains the number 1, now contains the number 3.
In the next step, the program decides to exit the loop if the condition is matched, en the example contador must be larger than 50 to exit the loop. If not, the program returns to the beginning of the loop.
ACTIVITY
Today you'll create a Raptor algorithm using two loops and a decision. The name of the file will be Student number + Loops and decisions
The main idea is to show the odd numbers between 1 and 50 or to show the pairs numbers between 2 and 50, the user will decide.
- When the program starts, it should ask the user to decide between odd or pairs. Use an Input Symbol and a Rhombus to create two paths.
- To use Loops you'll need a variable that changes its content in every cycle. In this activity that variable will be known as counter. This counter will increse by two every cycle.
- In every cycle, the algorithm shows the user the counter (variable) using a raptor output symbol.
- When the variable (counter) meets the established condition, the procedure will exit the loop and end the program.
- As always, when finished, turn in the file using the Classroom post.
CLASS NOTES
Write down in your notebook the title of the class, the objective and follow the instructions.
- Explain, using your own words, the repetitive coding(loops) and compair it to sequencial and decision coding.
- Imagine an every day problem that could be solve using loops coding.
- What is a Call in Raptor and how do we use it,?


.png)




.png)